Dentures are replacements for missing teeth that can be taken out and put back into your mouth. While dentures take some getting used to, and will never feel exactly the same as one’s natural teeth, today’s dentures are natural looking and more comfortable than ever.
There are two main types of dentures: full and partial. Your dentist will help you choose the type of denture that’s best for you based on whether some or all of your teeth are going to be replaced and the cost involved.
How do Dentures Work?
With full dentures, a flesh-colored acrylic base fits over your gums. The base of the upper denture covers the palate (the roof of your mouth), while that of the lower denture is shaped like a horseshoe to accommodate your tongue.
Dentures are custom-made in a dental laboratory from impressions taken of your mouth. Your dentist will determine which of the three types of dentures described below is best for you.
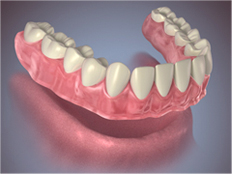
Conventional or Immediate Full Denture.
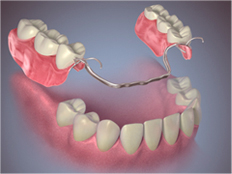
Partial Denture.
- Conventional Full Denture
A conventional full denture is placed in your mouth after any remaining teeth are removed and tissues have healed. Healing may take several months, during which time you are without teeth. - Immediate Full Denture
An immediate full denture is inserted immediately after the remaining teeth are removed. (Your dentist takes measurements and makes models of your jaw during a prior visit.) While immediate dentures offer the benefit of never having to be without your teeth, they must be relined several months after being inserted. The reason is that the bone supporting the teeth reshapes as it heals, causing the denture to become loose. - Partial Denture
A partial denture rests on a metal framework that attaches to your natural teeth. Sometimes crowns are placed on some of your natural teeth and serve as anchors for the denture. Partial dentures offer a removable alternative to bridges.




